CURP, RFC, and CLABE: Complete Mexico ID Guide (+ When to Use What)
- Clave Única de Registro de Población (CURP) handles individual identification within the government system.
- CFDI v4.0 requires exact RFC name and address matching against SAT’s database, making customer RFC validation critical for invoicing.
- Signzy's verification solutions integrate with official Mexican registries to validate RFC, CURP, and banking identifiers in real-time, streamlining compliance for businesses operating in México.
I was grabbing lunch with a consultant friend who had just finished helping a tech company set up its México operations.
‘You know what’s funny?’ she said, ‘Everyone panics about the Mexican bureaucracy, but their identification system is actually pretty logical once you see the big picture.’
She explained how this company had been dreading the compliance setup, expecting months of back-and-forth with government offices. Instead, they got everything sorted in a few weeks.
Curious, I asked what made the difference.
She mentioned that México uses specific identification codes that work together, and most companies struggle because they don’t understand this system upfront.
My curious brain couldn’t let it go, so I started asking around and doing some research. It turns out there’s a clear pattern – companies that nail their México setup versus those that struggle all come down to three codes: CURP, RFC, and CLABE.
Related Resources
We'll go through all three one by one. Before anything, here's a quick overview:
CURP, RFC, and CLABE - Quick overview
| Aspect | CURP | RFC | CLABE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Issued By | RENAPO (National Population Registry) | SAT (Tax Administration Service) | ABM/Banco de México (Banking Association/Central Bank) |
| Format | 18 alphanumeric characters | 12-13 alphanumeric characters | 18 numeric digits |
| Primary Business Use | Employee registration, legal representatives | Invoicing, contracts, tax filings | Wire transfers, vendor payments, payroll deposits |
| Required For | Payroll setup, HR systems | Business operations, bank accounts | Electronic fund transfers, SPEI payments |
| Verification/validation | RENAPO portal, SIgnzy CURP Verification API | SAT portal (up to 5,000 records), Signzy RFC Fetch API | Bank systems, CLABE validators |
💡The preferred approach is obtaining these codes in sequence: start with CURP since it’s required for RFC applications, then get your RFC for business operations, and finally set up your CLABE through banking once your business registration is complete.
Now, let’s discuss the specifics of each.
CURP: Everything you need to know
CURP represents the foundational identification code that Mexican businesses encounter in every employee hire, customer transaction, and compliance audit.
What is CURP?
CURP stands for Clave Única de Registro de Población, which translates to Unique Population Registry Code. This 18-character alphanumeric identifier serves as the primary identification number for all individuals registered within México's population registry system. RENAPO, the Registro Nacional de Población e Identificación Personal, issues and maintains CURP records for the entire country.
What is the CURP format and structure?
CURP contains 18 alphanumeric characters following the format XXXXYYMMDDXSSXXXXX, where each section encodes specific biographical information.
- Characters 1 to 4 – Name components: First letter of paternal surname, first internal vowel of paternal surname, first letter of maternal surname, and first letter of given name.
- Characters 5 to 10 – Birth date (YYMMDD format): Someone born on March 15, 1985, would have 850315 in these positions.
- Character 11 – Biological sex: H indicates male, and M indicates female.
- Characters 12 to 13 – State of birth: Two-letter codes represent birthplace, such as DF for México City or NL for Nuevo León.
- Characters 14 to 16 – Internal consonants: These positions contain the first internal consonant from the paternal surname, maternal surname, and given name, respectively.
- Character 17 – Numerical differentiator: RENAPO assigns this number to distinguish individuals with otherwise identical information.
- Character 18 – Check digit: A calculated validation digit confirms the entire CURP structure's accuracy.
💡 Related Blog:
How do you obtain a CURP?
Mexican citizens born in México receive CURP automatically through birth registration, while foreign residents and citizens born abroad must apply through RENAPO or Mexican consulates.
How is CURP different from other Mexican identification codes?
CURP serves exclusively as a population registry identifier, while RFC functions specifically for tax administration, and CLABE operates as a banking transaction code.
CURP versus RFC: Key differences
- CURP remains constant throughout a person's life. RFC status changes based on tax obligations and business activities
- CURP identifies people for government services. RFC tracks taxpayers for fiscal administration
- An individual's RFC typically incorporates their CURP's first ten characters, but adds additional tax classification elements.
- CURP is issued at birth or upon residency. RFC is issued when an individual begins taxable activities
CURP versus CLABE: Key differences
- CURP connects to the population registry system. CLABE connects to the banking system for electronic transfers
- CURP validates individual identity. CLABE facilitates account-specific payments
- CURP remains constant throughout life. CLABE numbers change when opening new accounts or switching banks
- RENAPO issues CURP. Financial institutions issue CLABE to account holders
What are the CURP compliance requirements for businesses in México?
Businesses must verify CURP of employees before payroll submissions, conduct customer due diligence in regulated industries, and maintain proper documentation to avoid penalties, including rejected filings and license suspensions.
CURP compliance: Employee verification requirements
- Collect CURP from all employees before submitting payroll to IMSS or calculating tax withholdings.
- Confirm each CURP exists in RENAPO's database and matches employee documentation.
CURP compliance: Customer due diligence requirements
- Verify customer CURP as part of Know Your Customer compliance in regulated sectors
- Confirm individuals exist in RENAPO records and check for deceased status
- Flag inconsistencies between personal details and official records
- Cross-reference information against multiple sources for high-value customers
- Monitor for identity fraud patterns like mismatched details or the use of relatives' documentation
CURP compliance: Documentation and record-keeping requirements
- Maintain original CURP verification results from RENAPO or authorized API providers with timestamps
- Keep records of any discrepancies found and resolution steps taken
- Store employee or customer consent forms for CURP collection
- Preserve audit logs showing who performed verification and what systems were accessed
CURP compliance: Ongoing monitoring requirements
- Verify CURP immediately during employee onboarding and customer account opening.
- Check the CURP status when individuals report corrections or updates
- Reverify for high-value transactions or account changes
How to verify CURP?
CURP authenticity can be verified through RENAPO's online portal or automated API services for high-volume operations.
RENAPO online verification portal
RENAPO provides a free online portal for basic CURP validation. Enter the complete 18-character CURP to receive the registered name, birthdate, and validity status from the official database. This method works well for occasional verifications but lacks the audit documentation required by regulated businesses.
"CURP verification was taking our team 10 minutes per customer with manual checks. Signzy does it in under 5 seconds. We onboarded 2,000 customers last month without a single compliance flag from CNBV." — Compliance Lead, México Fintech Platform (350+ employees)
Using Signzy’s CURP API
Signzy's México CURP Verification API provides instant validation against RENAPO's official database for businesses requiring scalable identity verification solutions. Key benefits include:
- Real-time fraud detection identifies forged numbers, synthetic identities, and benefit fraud attempts before they enter your system, stopping identity theft at the onboarding stage.
- Comprehensive data retrieval returns full personal details, including name, date of birth, gender, state of birth, CURP status, and registration information in a single API call.
- Seamless bulk verification processes hundreds of CURP checks simultaneously without manual lookups, reducing operational workload and accelerating customer onboarding workflows.
- Multi-language support accommodates diverse business environments while maintaining consistent validation standards across different user interfaces and regional operations.
- Compliance alignment with Mexican AML and KYC regulations ensures businesses meet CNBV requirements for customer identification and government oversight standards.
This API-driven approach delivers sub-5-second response times while maintaining data accuracy across millions of verified users.
RFC: Everything You Need to Know
The Registro Federal de Contribuyentes functions as México's tax identification system for individuals and businesses engaged in economic activities.
What is RFC?
RFC stands for Registro Federal de Contribuyentes, translating to Federal Taxpayer Registry. This 12 or 13-character code identifies taxpayers within México's fiscal system. SAT, the Servicio de Administración Tributaria (Tax Administration Service), issues RFC numbers and oversees all tax-related registrations across the country.
The code establishes a taxpayer's legal existence within México's fiscal framework.
What is the RFC format and structure?
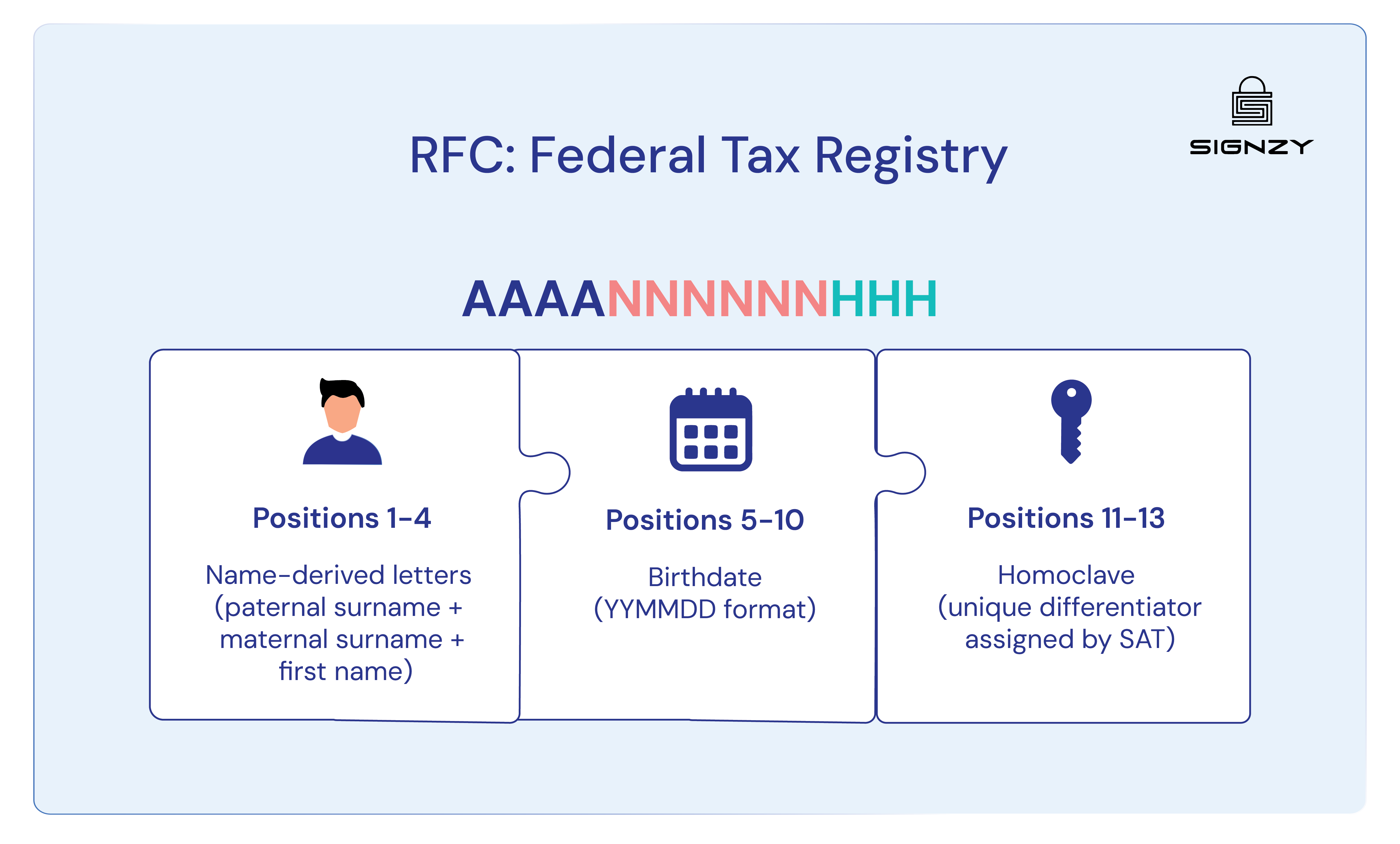
RFC follows either a 12-character format for individuals or a 13-character format for businesses, encoded as XXXX######XXX or XXXX######XXX# respectively.
- Characters 1 to 4 – Name or business designation: For individuals, this includes the first letter of the paternal surname, the first internal vowel of the paternal surname, the first letter of the maternal surname, and the first letter of the first given name. For businesses, these four positions contain abbreviations derived from the legal entity name.
- Characters 5 to 10 – Registration date (YYMMDD format): For individuals, this reflects the birthdate. For businesses, this represents the incorporation or formation date. Someone born on July 22, 1990, would have 900722 in these positions.
- Characters 11 to 12 – Homoclave: SAT assigns this two-character alphanumeric code to differentiate taxpayers with identical names and date information. The homoclave prevents duplicate RFC assignments within the system.
- Character 13 – Verification digit (businesses only): Business RFC includes an additional check digit that validates the entire code structure through mathematical calculation. Individual RFC stops at 12 characters without this verification element.
How do you obtain an RFC?
Mexican nationals obtain RFC through SAT's online portal at sat.gob.mx by providing their CURP, official identification, and proof of residence, receiving the certificate immediately for online applications or within 48 hours for in-person submissions.
Businesses require prior registration with the Public Registry of Commerce before completing SAT registration with incorporation documents, representative identification, and registered address proof, receiving a business RFC within 3 to 5 business days, alongside digital certificate capabilities for electronic filing.
How is RFC different from other Mexican identification codes?
RFC operates exclusively within the tax system, while CURP manages population registry functions and CLABE handles banking transactions.
RFC versus CURP: Key differences
- RFC identifies taxpayers for fiscal obligations. CURP identifies individuals for government services
- SAT issues an RFC when taxable activities begin. RENAPO issues a CURP at birth or upon establishing residency
- RFC incorporates CURP's initial characters for individuals, but adds fiscal classification data
- RFC status fluctuates based on tax compliance. CURP remains constant regardless of financial activities
- Businesses receive RFC but never receive CURP. Only individuals qualify for CURP registration.
RFC versus CLABE: Key differences
- RFC tracks taxpayer identity across all fiscal matters. CLABE identifies specific bank accounts for payment processing
- RFC remains consistent when changing banks. CLABE changes with each new account opening
- RFC appears on invoices and tax returns. CLABE appears exclusively in payment instructions and wire transfer forms
- One business holds one RFC. The same business may hold dozens of CLABE numbers across different accounts.
What are the RFC compliance requirements for businesses in México?
Businesses must validate RFC for all commercial relationships, maintain updated vendor registrations, and ensure invoice requirements meet CFDI standards to preserve expense deductibility and avoid tax penalties.
RFC compliance: Vendor and supplier validation
- Verify the vendor RFC exists in SAT's active taxpayer registry before establishing payment relationships.
- Confirm the vendor's registered business activities match the services or products they provide
- Check the vendor RFC against SAT's blacklist of non-compliant taxpayers quarterly.
- Validate that the vendor's fiscal address matches the incorporation documents and service delivery locations.
- Reject invoices from vendors showing suspended or inactive RFC status
RFC compliance: Customer invoicing requirements
- Collect accurate RFCs from all business customers requiring CFDI invoices for purchases.
- Verify customer RFC name matches SAT's Constancia de Situación Fiscal exactly.
- Confirm the customer's postal code aligns with RFC registration data to prevent invoice rejection.
- Use generic RFC codes for customers without tax registration: XAXX010101000 for Mexican individuals, XEXX010101000 for foreign customers.
- Implement real-time RFC validation during invoice generation to avoid CFDI rejections.
RFC compliance: Employee tax documentation
- Obtain RFCs from all employees for accurate tax withholding calculations and IMSS reporting.
- Verify employee RFC matches their CURP and official identification documents.
- Update employee RFC records when SAT notifies of changes or corrections
- Submit employee RFC to IMSS during initial registration and maintain synchronization across systems
- Preserve RFC validation records for labor audits and tax authority inspections
RFC compliance: Documentation requirements
- Maintain the current Constancia de Situación Fiscal for your business, showing active RFC status.
- Store vendor RFC validation results with timestamps for each business relationship.
- Keep records of invoice rejections and corrections related to RFC mismatches.
- Document RFC verification procedures in compliance manuals for audit readiness
- Preserve communication with SAT regarding RFC updates or status changes
How to verify RFC?
RFC verification occurs through SAT's validation portal or specialized API services for businesses requiring automated checks.
SAT online verification portal
SAT operates a free verification service at sat.gob.mx, where users validate RFC against official taxpayer records.
- Visit sat.gob.mx
- Enter the RFC and taxpayer name to receive confirmation of registration status, legal name, and fiscal address.
- The portal indicates whether the RFC appears as active, suspended, or listed on SAT's blacklist of non-compliant taxpayers.
This manual process suits occasional verifications, but becomes impractical for businesses validating multiple vendors or customers daily.
Using Signzy’s RFC API
Signzy's México RFC Check API enables instant validation against SAT's taxpayer database for businesses managing vendor relationships and customer invoicing operations.
- Complete taxpayer intelligence retrieves legal name, trade name, registration status, tax regime, compliance flags, and full registered address in one API call, eliminating multiple lookup requirements.
- Blacklist detection automatically identifies suspended accounts and SAT-flagged entities before payment relationships form, protecting expense deductibility and preventing audit complications.
- Single-endpoint validation combines RFC verification with enriched profile data, including entity type, registration date, and CURP linkage, reducing integration complexity and development time.
- Bulk processing capabilities handle high-volume vendor onboarding and customer invoice generation without manual intervention, scaling efficiently as business relationships expand.
This automated RFC validation ensures every business relationship begins with verified taxpayer credentials while maintaining compliance with SAT and CNBV regulations.
"Signzy’s RFC validation caught three fake business registrations in our first week. Companies with legitimate-looking paperwork but invalid RFC numbers. Saved us from major fraud losses and regulatory headaches." — Compliance Director, Payments (200+ employees)
CLABE: Everything You Need to Know
The Clave Bancaria Estandarizada functions as México's standardized bank account identification system for electronic fund transfers and payment processing.
What is CLABE?
CLABE stands for Clave Bancaria Estandarizada, translating to Standardized Banking Code. This 18-digit numeric code identifies specific bank accounts within México's electronic payment infrastructure. Banco de México, the country's central bank, oversees the CLABE system through the Asociación de Bancos de México (ABM), which coordinates implementation across all financial institutions.
Without CLABE, businesses cannot process vendor payments electronically, employees cannot receive direct deposit payroll, and customers cannot complete wire transfers or electronic refunds.
What is the CLABE format and structure?
CLABE contains 18 numeric digits following the format BBBCCCAAAAAAAAAAAAAC, where each section identifies specific banking and account information.
- Digits 1 to 3 – Bank code: These three digits identify the financial institution holding the account. Each bank operating in México receives a unique code from Banco de México, such as 002 for Banamex or 012 for BBVA México.
- Digits 4 to 6 – Branch code: These positions specify the particular bank branch where the account was opened. Branch codes help route payments to the correct institutional location within larger banking networks.
- Digits 7 to 17 – Account number: These eleven digits represent the individual account identifier assigned by the bank. This is the unique account number that distinguishes one customer's account from all others within the same branch.
- Digit 18 – Check digit: The final position contains a calculated control digit that validates the entire CLABE structure. Banks compute this digit using a specific algorithm that confirms all preceding digits form a valid combination.
How do you obtain CLABE?
Banks automatically generate and assign CLABE numbers when customers open accounts, with each account type receiving its own unique CLABE identifier.
How is CLABE different from other Mexican identification codes?
CLABE operates exclusively within the banking system for payment routing, while CURP identifies individuals for government services, and RFC tracks taxpayers for fiscal administration.
CLABE versus CURP: Key differences
- CLABE identifies bank accounts for electronic transfers. CURP identifies individuals within the population registry
- Banks issue CLABE to account holders. RENAPO issues a CURP at birth or upon residency
- CLABE changes with each new account opened. CURP remains constant throughout a person's life
- CLABE facilitates payment processing. CURP enables access to government services
- One person holds multiple CLABEs across different accounts. Each individual receives only one CURP.
CLABE versus RFC: Key differences
- CLABE routes funds to specific bank accounts. RFC identifies taxpayers for fiscal obligations
- Banks generate CLABE for payment infrastructure. SAT issues RFC for tax administration
- CLABE appears in payment instructions and wire transfers. RFC appears on invoices and tax returns
- CLABE must match the account holder's banking profile. RFC must match the taxpayer's fiscal registration
- Businesses hold multiple CLABEs for different accounts. Businesses hold one RFC for all fiscal activities.
What are the CLABE compliance requirements for businesses in México?
Businesses must validate CLABE accuracy before processing payments, maintain current account information for all payment relationships, and implement verification procedures to prevent transfer failures and compliance violations.
CLABE compliance: Payment validation requirements
- Verify CLABE check digit calculation before initiating any SPEI transfer to confirm structural validity.
- Confirm the bank code matches a valid financial institution registered with Banco de México.
- Reject payment requests containing CLABE that fail validation checks
CLABE compliance: Transaction monitoring requirements
- Track payment success rates across different CLABE to identify problematic account relationships
- Flag repeated failures to the same CLABE as potential fraud or account closure indicators
- Review CLABE information quarterly for vendors and employees to catch account changes
- Monitor for suspicious patterns like multiple payments to similar CLABE numbers
How to verify CLABE?
CLABE verification occurs through check digit validation that confirms structural accuracy, or through banking confirmation services accessed via business banking portals or API integrations. Contact your bank's corporate banking department or use their online verification tools to confirm the CLABE corresponds to an active account with matching holder information before processing payments.
| CLABE Component | Digits | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Code | 3 | Identifies financial institution |
| Branch Code | 3 | Specific bank location |
| Account Number | 11 | Individual account identifier |
| Control Digit | 1 | Validates entire CLABE |
Verify México CURP and RFC with Signzy
Thanks for reading through all the México compliance details with me! I know it’s a lot to digest, but getting these three codes right makes everything else so much smoother.
“Bulk verification mode is perfect for our compliance audits. Uploaded 5,000 existing customer CURPs, got validation results in minutes. Found 47 that needed re-verification. Would've taken weeks manually." — Risk Analyst, Remittance platform (250+ employees)
We have separate guides on RFC and CURP as well, so check out our related blogs below if you want to dive deeper into either topic.
And if you’re looking to automate RFC or CURP verification instead of handling it manually, Signzy can help automate that process as well (while staying compliant, of course!). If you want to see exactly how, book your demo here.
FAQ
What happens if we process payroll with invalid employee CURP numbers?
Can we use the same RFC for multiple business entities in México?
How do we handle CLABE verification for high-volume vendor payments?
Do we need customer RFC for all invoices or just certain transaction types?

Saurin Parikh
Saurin is a Sales & Growth Leader at Signzy with deep expertise in digital onboarding, KYC/KYB, crypto compliance, and RegTech. With over a decade of professional experience across sales, strategy, and operations, he’s known for driving global expansions, building strategic partnerships, and leading cross-functional teams to scale secure, AI-powered fintech infrastructure.







