How Deepfakes Bypass Biometric Verification? 6 Methods Exposed (2026)
- Deepfakes use AI to create synthetic media that bypasses biometric security through camera injection, voice cloning, face-swapping, and server compromise, exploiting systems that can't distinguish real from AI-generated content.
- Effective deepfake prevention requires advanced liveness detection, multi-layered verification, continuous monitoring, and specialized detection technology that identifies pixel-level inconsistencies and synthetic media artifacts in real-time authentication processes.
- Signzy delivers 97% accurate deepfake detection in under 5 seconds with modular capabilities including UBO identification and sanctions screening, serving 600+ global companies with pay-as-you-go pricing across 180+ countries.
Most biometric systems answer one question: Does this face, voice, or fingerprint match our records? They don't answer a second critical question: Is this coming from a real person right now?
That's how deepfakes work. They provide biometric data that matches verification requirements without requiring an actual person to be present.
Deloitte's Center for Financial Services projects that generative AI fraud will reach $40 billion in the United States by 2027, up from $12.3 billion in 2023. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 30% of enterprises will no longer consider face biometric verification reliable when used alone.
These numbers reflect what's happening right now.
Understanding how these attacks work is the first step to stopping them. That’s what we are covering in this guide. Below, you'll find how deepfakes trick different biometric technologies and which solutions actually work to detect AI-generated content in real-time.
Related Solutions
What is a deepfake?
Deepfake is AI-generated synthetic media that manipulates images, videos, or audio to make someone appear to say or do something they never actually did. Using advanced machine learning algorithms, deepfakes can convincingly replicate a person's face and mannerisms with remarkable accuracy.
Unlike simple photo editing or filters, deepfakes use artificial intelligence to create entirely fabricated content that appears authentic.
Why are deepfakes becoming a serious security threat?
Deepfakes have evolved from internet curiosities into sophisticated fraud tools that exploit the trust businesses place in biometric verification systems.
📸 Easy accessibility to personal biometric data
Social media platforms provide fraudsters with unlimited access to photos, videos, and voice recordings of virtually anyone. These publicly available materials give criminals everything they need to create convincing deepfakes without physically accessing the victim.
A few profile pictures and video clips are enough to generate synthetic media that can bypass facial recognition systems designed to verify identity.
🔒 Exploitation of static biometric data
Biometric security systems rely on physical characteristics that remain constant throughout a person's life, but this permanence creates a fundamental weakness that deepfakes exploit.
Once these unchanging features are compromised, they cannot be reset like a password.
💰 Low cost and high financial reward
Creating deepfakes requires minimal investment while offering substantial financial gains through identity theft and fraudulent account creation.
With this, criminals can use deepfakes to access bank accounts, approve large transfers, create fake business credentials, or impersonate executives in corporate fraud schemes, making the risk-reward ratio highly attractive for cybercriminals.
💡 Related Blog:
How do deepfakes trick biometrics?
Deepfakes bypass biometric security by exploiting systems that verify data matches but cannot determine if that data comes from a real person or AI-generated content.
Fraudsters use several distinct technical methods to target different vulnerabilities in authentication systems:
METHOD #1. Camera injection attacks
Camera injection allows fraudsters to feed fake video directly into verification systems by disabling the device's actual camera and replacing it with pre-recorded deepfake content or synthetic video streams. Here's how the attack unfolds:
- Attackers gain control of the camera system: Malware or security exploits disable the physical camera sensor, preventing it from capturing what's actually in front of the device during verification.
- Fake video replaces real camera input: Pre-recorded deepfake footage or live-generated synthetic media gets injected into the verification app, showing the victim's face instead of a genuine camera feed.
- System processes manipulated video as legitimate: Verification software receives the fake video, matches it against stored biometric data, and grants access without detecting that the source was compromised.
This works because verification software typically cannot distinguish between genuine camera feeds and injected video sources, treating both as valid input during the authentication process.
METHOD #2. Voice cloning and audio replication
Voice cloning creates synthetic audio that replicates a person's vocal characteristics by training AI models on existing voice recordings. Fraudsters collect audio samples from social media, video calls, or public recordings, then use AI to analyze pitch, tone, accent, and speech patterns.
The trained model generates new speech in the target's voice, producing responses that pass voice-based authentication checks. Verification systems compare the synthetic audio to stored voice patterns, confirm a match, and approve access without detecting that the audio was artificially generated.
METHOD #3. Face-swapping in real-time
Real-time face-swapping overlays one person's facial features onto another during live video by tracking facial movements and replacing them with the target's appearance. This face-swapping operates by this process:
- The fraudster positions themselves in front of a camera while face-swap software runs in the background
- Facial tracking algorithms monitor the fraudster's head position, expressions, and movements continuously
- The software maps the victim's facial features onto the fraudster's face in real-time, matching every movement
- The verification system receives video showing the victim's face making natural, responsive movements
- The system confirms the face matches stored biometric data and approves access
The verification system processes what appears to be a legitimate user completing identity checks, unable to detect that someone else controls the movements behind the digitally swapped face.
METHOD #4. Synthetic identity creation
Synthetic identity fraud generates completely fabricated identities using AI-created faces that do not belong to real people. The technology combines features from multiple real faces or creates faces based on learned patterns, producing realistic human faces that are entirely computer-generated.
These synthetic faces contain consistent biometric features that verification systems process as legitimate. The system approves the synthetic identity because the biometric data appears authentic and matches expected human facial patterns.
This allows criminals to create fraudulent accounts without stealing actual identities, as the verification system has no way to confirm whether the person actually exists.
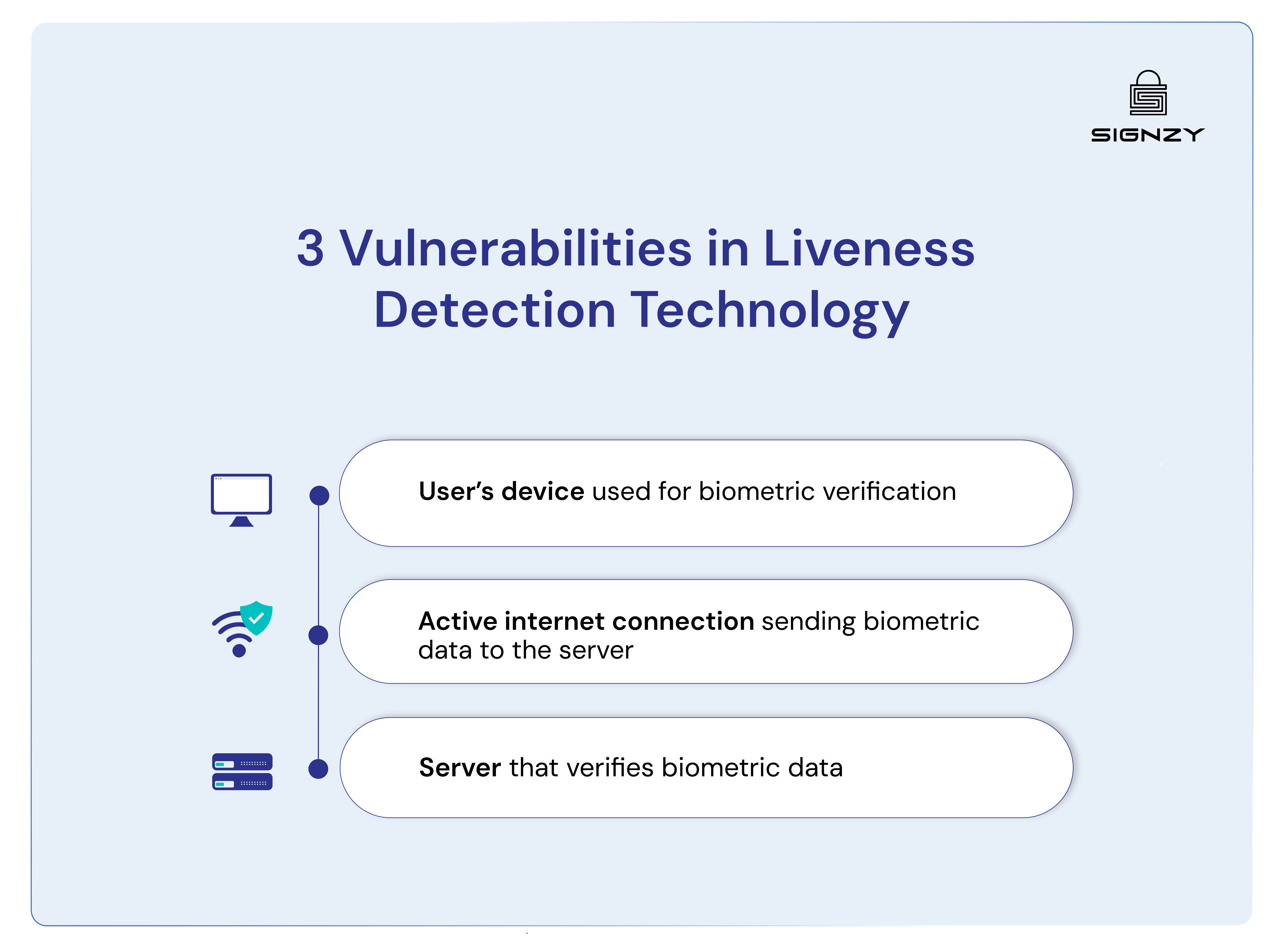
METHOD #5. Network interception attacks
Network interception captures and replaces biometric data as it travels from the user's device to the verification server, exploiting vulnerabilities in the transmission pathway.
Attackers position themselves between the device and server using man-in-the-middle techniques on unsecured Wi-Fi networks or compromised internet connections. Once positioned, they intercept the data stream, capture the legitimate biometric information being transmitted, and replace it with pre-prepared deepfake content before forwarding it to the authentication server.
The verification server receives the manipulated data, sees biometric information matching its records, and approves access without knowing the data was swapped during transmission.
METHOD #6. Server-side compromise
Server-side attacks target the authentication servers themselves rather than intercepting user data, giving fraudsters direct control over the verification system. Once attackers breach the server, they can manipulate the authentication process in several ways:
- Altering stored biometric templates - Hackers modify the reference data stored in databases to match their deepfakes, or inject entirely new fraudulent profiles into the system as legitimate user accounts.
- Changing verification logic - Attackers tamper with the authentication software itself, adjusting how strictly the system checks biometric matches or creating backdoors that automatically approve specific submissions.
Server compromise is the most severe vulnerability because it affects every user of the system simultaneously and can continue undetected for extended periods, enabling ongoing fraudulent access across countless accounts.
How resistant are different biometric technologies to deepfake attacks?
Mentioned below are a few ways that are easy and difficult for the potential AI threat to beat.
Algorithms for facial biometry: Simple to override
A face detection scanner is likely to be cracked if someone hacks it and places a deepfake in front of it. It confirms the identification of the deepfake using the static data kept in its system.
In the absence of layered liveness verification, deepfakes might be mistaken for the real user of the system by systems like iris recognition.
Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) is essential due to this additional weak point. The system is compatible with any device that has internet access, and MFA will allow biometric authentication methods to catch up.
With a single click, data theft can be stopped using a warning signal whenever someone attempts to access your restricted accounts from a different location or device.
Voice-controlled Security Systems: Difficult to override
Voice-controlled biometric devices are harder for deepfakes to fool. Voice activation is frequently used in conjunction with freshly created authentication questions that the AI is unable to figure out previously. Advanced systems can detect subtle vocal cord vibrations and breathing patterns that AI-generated voices struggle to replicate accurately.
Fingerprint Scanners: Not possible to override
Since deepfakes are all digital, they are considerably harder to fool fingerprint sensors. For deepfakes to bypass fingerprint sensors, attackers would need to compromise the scanner's software directly to inject fake fingerprint data that the system accepts as valid. Scanners use heat to confirm that a finger is placed on their surface.
Deepfakes can mimic fingerprints, but they are not able to produce heat that is comparable to that of a human hand.
How to protect yourself from AI-generated deepfakes?
Protecting against deepfake fraud requires moving beyond basic biometric checks to systems that can actually tell the difference between real people and AI-generated content. Here are the key defenses that work:
- Advanced liveness detection: Use verification systems that check for real human characteristics like subtle skin texture changes, natural eye movement patterns, and spontaneous micro-expressions that current deepfake technology cannot fully replicate during live verification.
- Multiple verification layers: Combine biometric checks with other security measures like one-time passcodes sent to verified devices, knowledge-based questions, or behavior analysis that tracks how users typically interact with systems over time.
- Deepfake detection technology: Deploy specialized deepfake detection systems trained to spot telltale signs of synthetic media, including pixel-level inconsistencies, unnatural lighting patterns, or artifacts that appear when AI generates faces, voices, or movements.
- Continuous monitoring and updates: Regularly update security systems to recognize new deepfake techniques as they emerge, track authentication patterns for anomalies, and flag verification attempts that deviate from normal user behavior or location patterns.
- Choose security providers carefully: Partner with vendors who actively research emerging deepfake threats, update their systems frequently to counter new attack methods, and provide comprehensive protection that evolves alongside the technology fraudsters use.
Deepfake technology will keep advancing, so static security measures that worked yesterday may not work tomorrow. Effective protection requires systems that learn, adapt, and stay current with evolving fraud techniques.
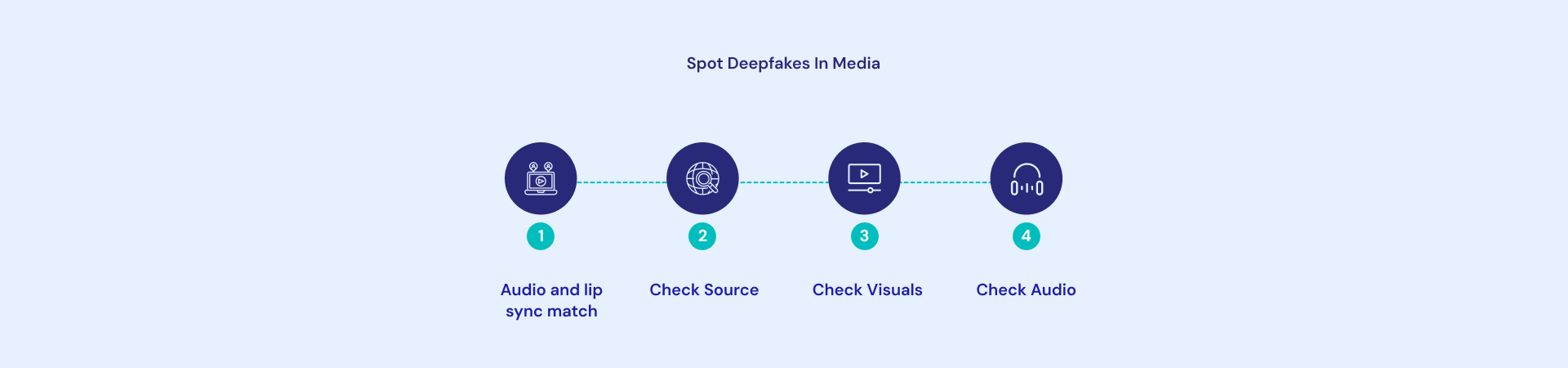
How to know you're dealing with a deepfake? Red flags explored
👁️ Unnatural eye movements or blinking patterns: Eyes that blink too frequently, not at all, or in a robotic rhythm rather than natural, irregular patterns humans display during conversation.
🎭 Facial inconsistencies at the edges: Blurring, distortion, or color mismatches where the face meets the hair, neck, or background, especially noticeable when the person moves their head.
💡 Strange lighting or shadows: Lighting on the face doesn't match the environment, shadows fall in the wrong directions, or skin tone appears unnaturally uniform without normal light variation.
🎤 Audio-visual synchronization issues: Lip movements that don't perfectly match spoken words, slight delays between mouth movement and sound, or unnatural pauses in speech rhythm.
📱 Pixelation or artifacts during movement: Image quality degrades when the person moves quickly, unusual pixel patterns appear around facial features, or glitchy distortions occur during head turns.
🌫️ Inconsistent background elements: Background appears static while the person moves, objects that seem frozen, or environmental details that don't react naturally to movement or lighting changes.
🗣️ Robotic or monotone voice patterns: Speech lacks natural emotional variation, breathing sounds that seem absent or artificially inserted, or pronunciation that sounds slightly mechanical.
Best solutions to prevent deepfake fraud
SOLUTION #1. Signzy's AI-powered deepfake detection
Signzy offers a comprehensive deepfake detection solution that combines active and passive liveness checks with AI-driven biometric verification to identify manipulated media in under 5 seconds.
The platform provides:
- Active and passive liveness verification: Choose between active prompts requiring user actions like smiling or head rotation, or passive analysis that works in the background, adapting verification methods based on time constraints, network conditions, and user experience requirements.
- Smart face match with AI-driven prompts: Advanced face match systems detect and prompt users to remove masks, glasses, or other face coverings, ensuring clear facial capture while identifying inconsistencies and potential manipulations in submitted media.
- Multi-layered fraud protection: Deepfake detection integrates seamlessly with identity verification APIs, document verification, and UBO checks, creating comprehensive protection against bad actors from the first customer touchpoint through ongoing monitoring.
- Frictionless three-step verification: Users capture selfies or perform requested actions, the system detects inconsistencies and manipulations instantly, then makes secure decisions to welcome legitimate users while blocking fraudsters without adding unnecessary friction.
Signzy's solution delivers high API accuracy with response times under 5 seconds, processing over 100 million user verifications while maintaining seamless integration through APIs that fit into existing workflows without requiring process overhauls.
“Someone cloned a client's voice and got us to wire a huge amount. That was our wake-up call. Since implementing Signzy, we've caught seven voice cloning attempts that would have cost us millions. Our wire fraud is essentially zero now." — VP of Client Services, Private Wealth Management Firm.
"Signzy caught what we completely missed. We had no idea deepfakes were even hitting our platform until their system flagged 23 attempts in the first two months. Turned out we'd already approved one that cost us $15,000. Since then, there have been zero successful attacks, and we've avoided roughly $280,000 in fraud. They are great at what they do!" — Head of Fraud Prevention, Digital Lending Platform.
SOLUTION #2. Jumio Liveness Premium with advanced deepfake detection
Jumio's liveness solution leverages patented technology combining randomized color sequences and AI-driven analysis to confirm human presence in real-time.
The solution employs sophisticated AI models trained to recognize and block advanced threats that traditional presentation attack detection methods miss. Early adopters report catching over 30% more sophisticated fraud attempts compared to previous systems.
The platform performs comprehensive document analytics using informed AI and machine learning models to detect manipulated government-issued IDs, synthetic IDs with AI-generated images, and sophisticated tampering undetectable to human eyes.
SOLUTION #3. HyperVerge single-image passive liveness detection
HyperVerge's single-image passive liveness detection requires users to capture just one selfie without performing any gestures or actions. This approach analyzes the single image for complex characteristics, including light patterns, skin texture, micro-motions, and biological signals that deepfakes struggle to replicate accurately.
HyperVerge's system provides immediate, actionable feedback when users capture non-compliant selfies, prompting them to adjust lighting or angles before resubmission rather than rejecting attempts outright.
What makes Signzy's deepfake detection different?
Start with the basics: Signzy catches deepfakes, face swaps, and injection attacks with 97% accuracy in real-time. Response times stay under 5 seconds. Active and passive liveness checks work as they should.
That foundation is solid, but fraud prevention needs more than just confirming a real person is present.
The difference is modularity. Businesses don't need every verification capability on day one. You might start with deepfake detection, add document checks in quarter two, include sanctions screening when compliance requirements change, then layer in business verification as partnership volume grows.
"Signzy helped us win back clients we'd lost. After a major data interception incident cost us a huge contract, their real-time detection gave us credibility again. We've recovered three lost clients and haven't had another breach." — CEO, Financial Services Platform.
Signzy lets you build this way. Each new capability integrates with existing KYC or KYB processes without replacing your entire verification stack. Geographic expansion doesn't require hunting for regional providers. One API covers 180+ countries.
Over 600+ global companies, including 10+ Fortune 30 organizations, rely on this approach because Signzy adapts to their verification needs rather than forcing them into fixed solutions.
To know more about how exactly Signzy can help, book a demo here.
FAQ
Is deepfake detection legally required yet?
What if a real user gets flagged as fake?
Can attackers beat deepfake detection with stronger AI?
Do we need special devices for liveness checks?
Are deepfakes only a banking issue?

Priyabrata Pradhan
Priyam serves as VP of Engineering at Signzy, overseeing API platform engineering, infrastructure, security and global product delivery. With an experience of 16+ years in building fintech-grade tech stacks, microservices and scalable architectures, he ensures that Signzy’s identity-verification, compliance and global-expansion products consistently meet high performance, security and regulatory standards across markets.



![Face Matching vs. Selfie Verification [Which is Right for You?]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/blrzl70g/production/35569107cd3d0dc0e28b221813f008c8301a7f78-2560x600.webp)
