Biometric Passport vs Optical Passport: What’s the Difference?
- Biometric passports are significantly more difficult to counterfeit due to encrypted chips and digital signatures. Optical passports rely mainly on visual security features that can be replicated more easily.
- Modern biometric passports include multiple security layers like Basic Access Control and RF blocking to prevent unauthorized scanning. However, older versions may have fewer protections.
- Manual verification of optical passports typically takes 2-3 times longer than automated biometric scanning. The exact difference depends on your staff training and document complexity.
Most businesses handle two different kinds of passports without realizing it. Some passports still work the traditional way – your team visually checks the photo against the person. Others come with small digital chips that can connect directly to your verification systems and pull up data automatically.
This difference opens up some interesting opportunities. Companies that understand how to work with both types often see faster processing times and smoother client experiences. The digital ones, especially, can streamline a lot of the manual work your team currently does.
If you’re handling international clients, new hires from abroad, or any cross-border verification, knowing which type you’re working with can help you choose the right tools and processes to make everything run more efficiently.
Before discussing all key differences, let’s understand how both – biometric and Optical – passports work.
Related Resources
What Are Biometric Passports?
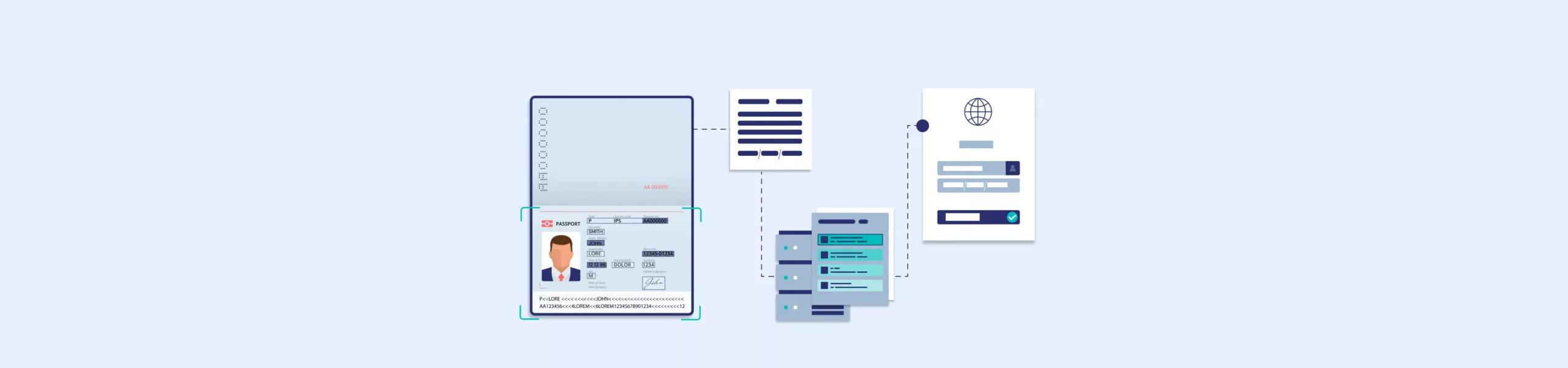
Biometric passports have a microchip embedded inside that stores personal data along with biometric information like facial images, fingerprints, and iris scans. A small gold camera symbol on the cover indicates it’s a biometric passport.
The chip communicates wirelessly with scanning equipment using RFID technology. This means your staff can extract all passport data and verify identity without manual data entry or visual comparison.
The verification process is straightforward: scan the passport near an RFID reader, and the system automatically pulls the stored information. Many systems can also compare a live photo of the person against the facial data stored on the chip.
What Are Optical Passports?
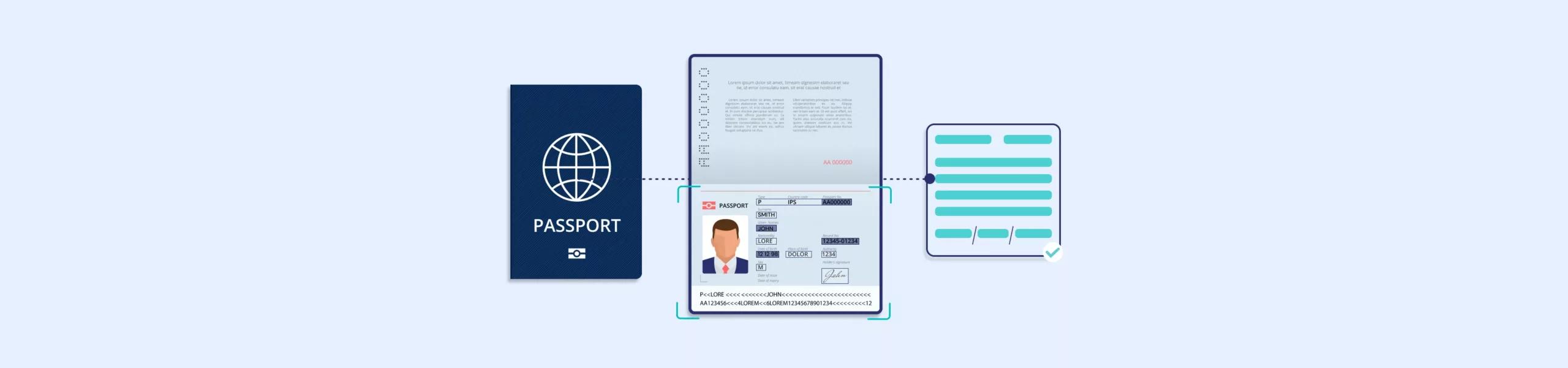
Optical passports have those two weird lines of text at the bottom that look like computer code. That’s the machine-readable zone where all your basic info gets encoded – name, birth date, passport number, that sort of thing.
Scanners can read those lines automatically instead of someone typing everything in by hand. Saves time and cuts down on typos. But here’s the catch – someone still has to look at your face and compare it to the photo. No getting around that human element.
For businesses, these mean more work for your team. Someone has to actually examine each document and make judgment calls about whether the person matches the photo. It’s not terrible, but it’s definitely more hands-on than the automated options you get with biometric passports.
💡 Related Blog:
Biometric vs Optical Passports – Key Differences
Your business will encounter both passport types during verification, and each requires different handling approaches that directly impact your operations, costs, and security.
1. Security Features
Biometric passports pack serious anti-fraud tech. The chip itself is locked down with encryption, and tampering with it leaves digital fingerprints that verification systems can detect. Try to mess with the data. The system knows.
Optical passports rely on visual security features – special inks, holograms, that sort of thing. The problem is that these depend entirely on your staff being trained to spot fakes. Miss a detail, and fraudulent documents slip through.
2. Verification Speed
With biometric passports, customers scan their documents and look at a camera. The software handles the comparison automatically. Takes seconds, not minutes.
Optical passports require your team to manually check the photo against the person, examine security features, and verify the scanned data makes sense. Each verification eats up more staff time and creates bottlenecks during busy periods.
3. Data Accuracy
Biometric systems pull information directly from the chip with built-in error checking. The data either matches or it doesn’t – no gray areas.
Optical verification introduces human judgment calls. Did someone gain weight? New haircut? Your staff has to decide if differences are normal changes or red flags, leading to inconsistent decisions across your team.
4. Technology Requirements
Biometric verification needs specialized RFID readers or NFC-enabled devices. More expensive upfront, but the automation pays off through reduced labor costs.
Optical systems work with basic document scanners that most businesses already own. Lower tech costs, but you’re trading equipment savings for higher ongoing labor expenses.
5. Cost Considerations
Biometric setups cost more initially, but process customers faster with fewer staff members needed for verification tasks.
Optical systems seem cheaper until you factor in the employee time spent on manual checks, training costs, and the business impact of slower customer processing.
6. Integration Capabilities
Biometric verification connects easily to automated systems and databases. Customer data flows directly into your existing workflows without manual data entry.
Optical verification typically requires someone to review results and manually input information into your business systems, creating extra steps and potential errors.
7. Fraud Prevention
Biometric passports make identity theft much harder. Faking biometric data requires sophisticated equipment and expertise that puts it beyond most fraudsters.
Optical document fraud happens more often because the security features can be replicated with enough time and resources. Your business bears more risk when accepting these documents.
Setting Up Your Passport Verification Process
As said earlier, both passport types remain in circulation. Therefore, your verification system needs to accommodate both formats while maintaining security standards and operational efficiency.
Step 1 – Assess Your Document Volume and Risk Level
Start by tracking how many passports you process monthly and what types you’re seeing. Most businesses handle a mix. Higher volumes justify automated equipment costs, while smaller operations might stick with smartphone-based solutions.
Consider your fraud exposure. Financial services and high-value transactions need stricter verification than basic age confirmation. Document the specific compliance requirements for your industry – some regulations mandate biometric verification for particular transaction types.
Step 2 – Choose Equipment That Handles Both Document Types
Your scanner requires optical character recognition for the machine-readable zone on both passport types, as well as RFID capability for biometric chips. Mid-range document readers start around $2,000 and handle both formats effectively.
Smartphone apps offer a budget alternative for lower volumes. These use the phone’s camera for OCR scanning and NFC for biometric chips. Quality varies significantly between providers, so test thoroughly with your actual document mix before making a commitment.
Step 3 – Design Your Staff Workflow
Create a two-track process. When someone presents a passport, your staff first identifies the type – biometric passports have that camera symbol, but optical ones don’t. This determines which verification steps to follow.
For biometric passports, scan the chip, capture a live photo for facial comparison, and let the system handle verification. For optical passports, scan the machine-readable zone, manually compare the image to the person, and verify visible security features, such as holograms.
Step 4 – Set Up Data Validation Rules
Program your system to cross-check extracted data against your customer database and external verification services. Flag obvious inconsistencies:
- Birth dates that don’t match
- Names with different spellings
- Your passport numbers are already in our system.
Build in manual review triggers for edge cases. Some situations will always need human judgment, like determining if appearance changes are normal aging or potential fraud indicators.
Step 5 – Plan Your Integration Strategy
Connect your verification system to existing customer databases and compliance reporting tools. Automated data flow reduces errors and speeds up processing.
Consider connecting to verification services where available. These provide additional fraud protection by checking passport numbers against official databases, adding an extra security layer for both document types.
Streamline Your Passport Verification with Signzy
Most businesses require systems that can handle both types of passports, as you can’t control which documents customers present. Focus on solutions offering OCR for optical passports and RFID capability for biometric ones.
Signzy’s AI-powered platform automatically handles both biometric and optical passports, as well as other document types from over 240 countries. Our solution instantly detects passport types and applies the correct verification method: RFID scanning for biometric documents and enhanced security checks for optical ones.
Beyond passport verification, obtain a comprehensive KYC suite, including face matching, document authentication, and AML screening. Integrate directly into your workflows and reduce verification time from minutes to seconds.
FAQ
Can I tell if someone has a biometric or optical passport just by looking at it?
Do I need different equipment to scan both types of passports?
Are optical passports still valid for business verification?
What information can I extract from each type of passport?

Gaurav Gupta
Gaurav Gupta is the Global Product Head at Signzy, leading the strategy and development of the company’s KYC, KYB, AML, and digital onboarding products used by banks, fintechs, and financial institutions across global markets. He specializes in building scalable compliance and verification platforms, transforming complex regulatory and risk workflows into seamless, automated product experiences. Gaurav works at the intersection of product, engineering, and AI.



![7 Best Passport Verification Solutions [2026 Rankings]](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/blrzl70g/production/23de260f1b00a6852d34dccf5febbcf942457675-2821x663.webp)