How we replaced legacy banking processes with AI-driven technology
Signzy — Building Global digital trust system using AI & Blockchain
One such interesting use case we encountered recently was about an id verification software. Given an image of an identity card the algorithm has to classify it to one of the following classes..
- Aadhaar
- PAN
- Driving License
- Passport
- Voter Id
In this blog post we will take you to behind-the-scenes of our state-of-the-art system and how we tackled the problem, ultimately overpassing the targeted accuracy required for real world use.
Knowing the beast we are to fight
As soon as we began to dive deeper into understanding the problem and identifying techniques we would use to attack it, we realised the most important constraints of the id verification software that we had to work within and the aim we are striving to achieve.
The idea is to deploy the pipeline into financial institutions with all possibilities of input variation and yet it should surpass or at least be equivalent to accuracy of a human being. The solution is to work on data which arrives from the most rural parts with pics taken from even 0.3 MegaPixel cameras and travelling over a dramatically slow connectivity. We knew the toughest challenge was to cater to variations that could arrive in inputs.
Humans have evolved intelligence for thousands of years, and created the systems to be easily processed by themselves. Take for instance an identity card. It is designed in dimensions to sit in pocket wallet, color formats to be more soothing to human eyes, data format which could sit well read by humans. If the Identity cards were designed to be consumed by a computer vision software it would have been an easier game, but since that’s not the case it becomes especially challenging.
We talked with different on-ground stakeholders to identify variations in input to the id verification software. Collecting initial samples wasn’t that hard, since a lot of these variations were told by our end users, but we knew creating training data is not going to be easy. We realized this quickly and started creating exhaustive training data in heavily curated and precisely controlled laboratory settings. We were able to get desired training sets successfully, which was half the problem solved.
World is not the cozy laboratory, we know that!
Our target was to create an id verification software which could be more than 99% accurate and yet be fast enough to make an impact. This isn’t easy when you know your input is coming from the rural end of India and you won’t have high end GPUs to process on (As a matter of fact, our largest implementation of this solution runs without GPUs).

A gist of environment where our input is created
The id verification app is expected to perform well in different sorts of real world scenarios like varying viewpoints, illumination, deformation, occlusion, background clutter, less inter-class variation, high intra-class variation (eg. Driving License).
You can’t reject an application by an old rural lady, who has brought you a photocopy of printout which in turn is obtained from a scanned copy of a long faded PAN card. We took it as a challenge to create the system so that it can help even the rural Indian masses.
A few samples that we expect as input into our system are here:

Fig(1): Few samples our expected input data
The number of samples we have for training is a huge constraint, you only have so much time and resources to prepare your training data.
Creating the id verification software
Baby steps ahead
We tried out various online identity verification methods for solving the problem. Firstly we extracted features using Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) feature extractor from OpenCV and then trained a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier on top of the extracted features. The results were further improved by choosing XGBoost classifier. We were able to reach about 72% accuracy. We were using Scikit learn machine learning framework for this.

Not enough, let’s try something else
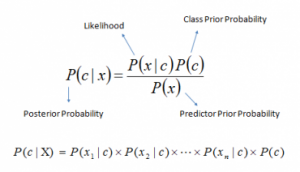
In our second approach, we tried ‘Bag of words’ model where we had built a corpus containing unique words from each identity card. Then we feed the test identity cards to an inhouse developed OCR pipeline to extract text from the identity card. Finally we input the extracted text to a ‘Naive bayes’ classifier for the predictions. This method boosted the accuracy to 96% . But the drawback of this approach was that it can be easily fooled by hand written text.

Taking the deep learning leap
“The electric light did not come from the continuous improvement of candles.” — Oren Harari
In the next approach we trained a classical Convolutional Neural Network for this image classification task. We benchmarked various existing state of the art architectures to find out which works best for our dataset eg. Inception V4, VGG-16, ResNet, GooLeNet. We also tried on RMS prop and Stochastic Gradient Descent optimizers which did not turn out to be good. We finalized on ResNet 50 with Adam optimizer, learning rate of 0.001 & decay of 1e-5. But since we had less data our model could not converge. So we did a transfer learning from “Image net”, where we used the existing weights trained originally on 1 million images. We replaced the last layer with our identity labels and freezed the remaining layers and trained. We noted that still our validation error was high. Then we ran 5 epochs with all layers unfreezed. Finally we reached accuracy of around 91%. But still we were lagging by 9% from our target.

Hit the right nail kid, treat them as objects
The final approach is where the novelty of our algorithm lies. The idea is to use an image object detector ensemble model for image classification purpose. For eg. the Aadhaar identity has Indian Emblem, QR code objects in it. We train an object detector for detecting these objects in card and on presence with a certain level of confidence we classify it as a Aadhaar. Like this we found 8 objects which were unique to each identity. We trained on state of the art Faster Region Proposal CNN (FRCNN) architecture. The features maps are extracted by a CNN model and fed into a ROI proposal network and a classifier. The ROI network tries to predict the object bounding box and the classifier (Softmax) predicts the class labels. The errors are back propagated by ‘softmax L2 loss function’. We got good results on both precision and recall. But still the network was performing bad on rotated images. So we rotated those 8 objects in various angles and trained again on it. Finally we reached an accuracy of about 99.46% . We were using Tensorflow as the tool.
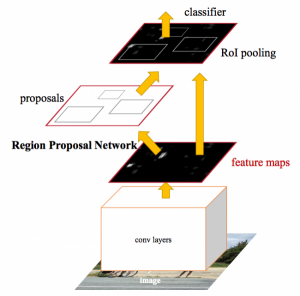
Fig(7): FRCNN architecture from original paper
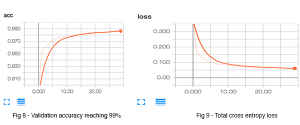

But we were yet to solve one final problem i.e the execution time. It took FRCNN approximately 10 seconds to classify in a 4 core CPU. But the targeted time was 3 seconds. Because of the ROI pooling the model was slow. We explored and found out that Single shot multibox detector (SSD) architecture is much faster than FRCNN as it was end-to-end pipeline with no ROI layer. We re-trained the model in this architecture. We reached accuracy of about 99.15%. But our execution time was brought down to 2.8s.

Fig(12): SSD architecture from original paper
Good work lad! What next?
While the pipeline we had come up with till here has a very high accuracy and efficient processing time, it was yet far from the a productionised software. We conducted multiple rounds of quality checks and real world simulation on the entire pipeline. Fine-tuning the most impactful parameters and refining the stages, we have been recently been able to develop a production ready, world class classifier with an error rate less than human and at a much much lesser cost.
We are clearly seeing the impact deep learning can have on solving these problems which we once were unable to comprehend through technology. We were able to gauge the huge margin of enhancement that deep learning provides over traditional image processing algorithms. It’s truly the new technological wave. And that’s for good.
In the upcoming posts, we will share our story on how we tackled another very difficult problem — Optical Character Recognition (OCR). We are competing with global giants in this space including Google, Microsoft, IBM and Abby and clearly surpassing them in our use cases. We have a interesting story to tell over “How we became the global best in enterprise grade OCR“. Stay tuned.
Thank you.
Signzy AI team
Be part of our awesome journey
Do you believe that the modern world is driven by bits and bytes? And think you can take it on? We are looking for you. Drop us a note at careers@signzy.com.
Summary view
- Real world is not your laboratory, training data needs to be diverse and needs better outlier handling
- Deep learning requires you to be patient but once it starts getting effective it gives your exponential returns
- In a narrow use case you can beat a global giant with all the computing power in the world.
So future of deep learning is not commoditized products but adoption of deep learning in use cases as a tool to bring intelligence across the board. Deep Learning has to be company culture and not just a ‘tool’.
About Signzy
Signzy is a market-leading platform redefining the speed, accuracy, and experience of how financial institutions are onboarding customers and businesses – using the digital medium. The company’s award-winning no-code GO platform delivers seamless, end-to-end, and multi-channel onboarding journeys while offering customizable workflows. In addition, it gives these players access to an aggregated marketplace of 240+ bespoke APIs that can be easily added to any workflow with simple widgets.
Signzy is enabling ten million+ end customer and business onboarding every month at a success rate of 99% while reducing the speed to market from 6 months to 3-4 weeks. It works with over 240+ FIs globally, including the 4 largest banks in India, a Top 3 acquiring Bank in the US, and has a robust global partnership with Mastercard and Microsoft. The company’s product team is based out of Bengaluru and has a strong presence in Mumbai, New York, and Dubai.
Visit www.signzy.com for more information about us.
You can reach out to our team at reachout@signzy.com
Written By:
Signzy
Written by an insightful Signzian intent on learning and sharing knowledge.



