How do we tell what’s real in a world when it only takes minutes to make a virtual copy of a person?
Isn’t it strange?
Deepfakes are a reality despite their seeming dystopian science fiction nature- causing severe social, financial, and reputational harm.
AI creates deepfakes – synthetic media that include text, audio, video, and image generation. Deepfakes are typically personal images or videos that have been digitally altered by cybercriminals to deceive. Deepfakes can show people saying or acting in ways that they never had or would have.
You have probably noticed that more realistic deepfakes are appearing on your social media feed as a result of recent advancements in AI used to make deepfakes and the spread of inexpensive and simple deepfake generators.
Alternatively, perhaps more worrisomely, you have not noticed 🙂
Deepfakes are getting better as AI gets better
In April 2018, a video combining the photo of Barack Obama and Jordan Peele’s voice got viral – demonstrating the advancements in deepfake video technology.
“We’re entering an era in which our enemies can make it look like anyone is saying anything at any point in time,” warned Jordan Peele, who played Obama in the video- in reality they had never expressed those opinions.
Deepfake technology is developing and developing.
As a result, becoming more harmful.
Because of AI.
AI is capable of self-improvement, unlike “traditional” technology, which needs time and efforts to advance.
Yet, AI’s capacity for self-improvement has drawbacks. It is amazing if an AI can be made to do something good!
But the risk is unparalleled when an AI is built for something bad (like deepfakes).
What issues do deepfakes create?
Deepfakes can be used for various evil intents.
Like?
Hoaxes, election manipulation, reputation tarnishing and so on.
They can also be used for phishing or monetary scams, such when someone uses deepfake audio messages that seem to be from authoritative people.
They can also be used in situations of blackmail or extortion, in which the threat is the publication of a damaging but phoney picture.
The general suspicion that deepfakes instil in society against all sources of information, even reliable news sources, is an even bigger problem.
People can now assert that the media in issue is a deepfake if they are exposed as having committed crimes in reputable images, videos, or audio recordings.
Furthermore, the inability to identify ‘real’ from ‘fake’ could lead to uncertainty regarding – almost all activities.
Understanding the mechanics of deepfakes
Deepfakes are a combination of “deep learning” and “fake – using AI to convincingly create or modify audio, video, or photo.
They sort through a lot of genuine media using deep learning algorithms to simulate voice and facial gestures.
With the use of this technology, it is possible to transfer a person’s voice and facial expressions onto another, producing convincing ‘fake’ content that is harder and harder to differentiate from the ‘real’ content.
A Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) contains a large amount of data, such as numerous photos and videos, of the target person to create a deepfake.
The generator, which generates new data, and the discriminator, which compares the generated data to actual data to improve the output, are two components of this network.
Diffusion models are currently used in other methods, which produce realistic data through an alternative mechanism.
Furthermore, less complex techniques that make use of autoencoder models—which are less complex than diffusion models or GANs—also exist.
Identity verification services are facing a major challenge – because of the development of deepfake technology, which may be used to convincingly falsify identification documents or impersonate people.
Deepfakes are a worrying tool for financial crime in the digital sphere – because of how simple they are to create and how deceptive they can be.
How to spot deepfakes
In an effort to combat false information, businesses nowadays are offering watermarked credentials as deepfakes become more and more common online.
💡 Related Blog: How Fraudsters Leverage AI and Deepfakes for Identity Fraud
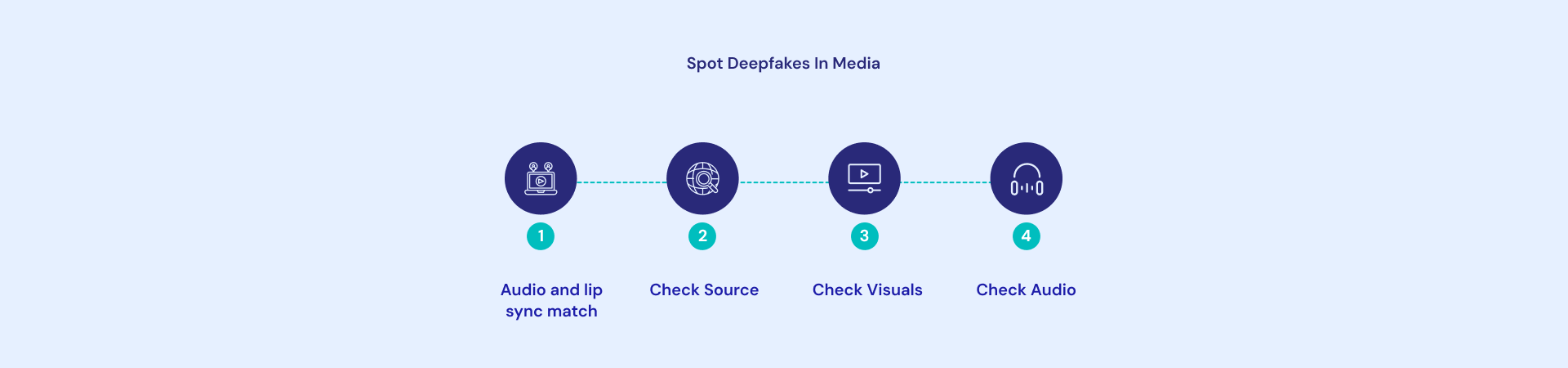
The issue: Deepfake technology is improving, making it more difficult to distinguish between fake and real. These four indicators are present.
Step 1: Check if the audio and lip sync match up with the video
Deepfakes produced by AI are not always able to perfectly sync their mouth movements with the audio. Thus, it could be a deepfake if you are watching a video and the sound seems a little strange.
Remember the deepfake film produced by Canny AI, an Israeli firm- in which Mark Zuckerberg was accusing Facebook of controlling and stealing people’s data by using video from a 2017 lecture. Even though it is a convincing deepfake, it becomes clear as you watch that the audio and speech are a touch off- indicating the fakeness in it.
Step 2: Check the source
The material’s source can be used to quickly determine whether something is a deepfake.
Step 3: Check the visuals
A video’s visual elements might reveal a lot about it. Examine the subject’s lighting, posture, background, and head and body placement to determine if it is a deepfake.
In March 2022, deepfake videos appeared on the internet purporting to depict Ukrainian President Zelensky advocating for the country’s submission to Russian forces. Many Ukrainians chuckled at the shoddy recordings and quickly understood they were fakes because –
Zelensky had two distinct light sources shining on his head and neck. His head remained in the same spot and appeared somewhat out of place. His body remained still. Overall, the image was hazy. There were moments when his face appeared to be ticking or twitching.
Step 4: Check the audio
Most people concentrate on the visual elements of a deepfake, but occasionally the clues can also be heard. Some telltale signs that you might be watching a deepfake include choppy sound, shifting audio levels, and an unnatural feeling in the speech.
If the speaker in the video appears to be sighing or breathing hard, pay close attention to any breath sounds—or lack thereof.
Future-proofing identity verification with deepfake detection
The threat posed by deepfakes is real and getting worse in the quickly changing digital landscape.
Fortunately, there are methods for identifying these fakes.
Deepfakes can be identified easily by attentively studying facial expressions, making sure the lips are in time with the audio, and searching for any strange lighting.
User security must be a top priority for both businesses and organisations, incorporating cutting-edge techniques like live verification procedures and deepfake detection technologies.
Signzy provides end-to-end identity verification software with liveness checks and the quickest deepfake detection in the industry.
When combined with document verification, biometric (identity) verification adds an extra degree of security. When a face biometric and a photo ID are compared, it can be ascertained that-
1) someone is indeed trying to register for a service and
2) the identity document belongs to the person presenting it.
Businesses are placing an increasing amount of emphasis on combating identity fraud caused by deepfakes.
As deepfakes are expected to persist in complicating identity verification procedures, it is critical to remain at the forefront of technology and knowledge.
Organisations can better prepare themselves to mitigate risks and guarantee the integrity and security of identity verification processes in the digital age by knowing the mechanics and ramifications of deepfakes.