- Money Service Businesses or MSBs operate in the same domain as banks and other financial institutions.
- MSBs provide a more niche range of services to individuals and businesses.
- FinCEN has over 30,000 MSBs registered with it.
We’ve discussed in multiple articles so far how money transfer and conversion are often used in money laundering. These transactions allow the money being laundered to be distanced from its illegal sources.
Over the years, Money Service Businesses, or MSBs have become something of a phenomenon. According to an article by PayDo, there are over 30,000 MSBs registered with FinCEN. These MSBs bring vital financial services to many citizens of the US. These services include the same transfers and conversions that aid money laundering. This is why the US regulations make it so that MSBs are subject to the same laws and rules as banks and other financial institutions. Today, we take a deeper look at MSBs and the regulations your MSB needs to be aware of and follow.
What is a Money Service Business?
To better understand how an MSB interacts with a country’s law, you need to understand the intricacies of an MSB. MSBs provide services like transfer, conversion, exchange, check encashing, and more. You see, these operations make it similar to banks and other financial institutions, but not the same. As a result of this similarity in operations, FinCEN’s new AML and CFT regulations apply to MSBs as well.
How are MSBs different from banks?
It must be noted that MSBs are similar to banks, but they are not the same. While banks cater to a wide array of financial requirements of their customers, MSBs provide more niche and specific services. MSBs mostly deal in the transfer and remittance of funds among their customers. Banks, on the other hand, provide more services like accepting deposits, extending loans, and more, on top of services that MSBs provide as well.
MSBs are still considered financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and need to comply with the same rules and regulations as them. Below are the types of businesses that these rules and regulations apply to.
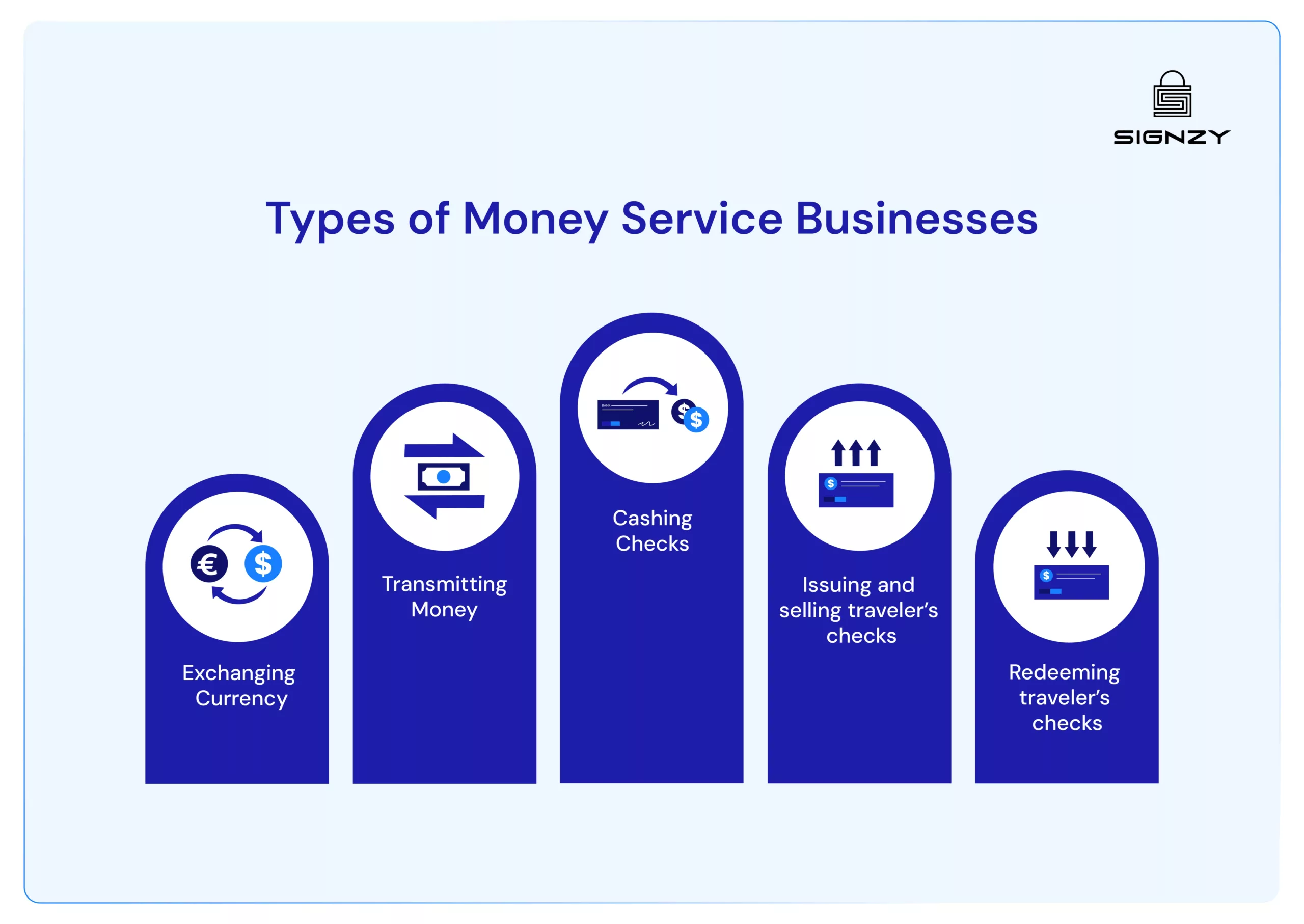
What are the Types of Money Service Businesses?
If your business provides the following financial services, they will be identified as an MSB:
- Exchanging Currency
- Sending and receiving (Transmitting) Money
- Cashing Checks
- Issuing and selling traveler’s checks, prepaid cards, or money orders.
- Redeeming traveler’s checks, prepaid cards, or money orders.
These businesses are considered MSBs by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) and need to meet the regulations and obligations set by FinCEN. These are the services that a business may provide to be considered an MSB. Now, let’s take a look at the businesses that are considered MSBs.
Examples of Money Service Businesses
The following businesses are considered MSBs and need to comply with the FinCEN’s regulatory requirements.
- Payment Processors: Payment processors are platforms that allow the transfer of funds between businesses, individuals, and other entities. Stripe, PayPal, and Square are some of the businesses that fall under this category.
- Remittance Processors: If your business captures invoices, coupons, bills of sales, and other payment documents and processes them, it falls under the category of a remittance processor. Payall Payments Systems, PayCruiser, Blaze Payments, and others operate under this umbrella of MSBs.
- Money Transfer Businesses: Money transfer businesses include players like Western Union, Wise, Revolut, and others. These businesses handle the transfer of money across various channels like brick-and-mortar, online, and overseas.
- Currency Exchanges: Currency exchanges allow people to buy and sell foreign currencies using the currency of their country. Airwallex, Finzly Inc, Rapyd, and others are examples of businesses operating in the currency exchange sector.
The types and examples of MSBs might be something you already know about. What’s important is to know the regulations that apply to your business should it happen to be an MSB. So let’s take a look at the regulations that apply to MSBs.
Applicable Regulations for Money Service Businesses
As we mentioned before, MSBs provide services that can be exploited by bad actors at every step of the money laundering process. The FinCEN supervises MSBs in the US, and they need to comply with the standards and regulations set by it under the Bank Service Act and other regulations. Compliance with the various laws and regulations that apply to MSBs can help your business avoid legal liabilities and monetary losses.
Let’s take a look at the various regulations that apply to MSBs:
Risk-based AML Approach
The new AML and CFT regulations require banks and financial institutions to take a risk-based approach. This risk-first approach also applies to MSBs that need to take sufficient measures to flag, avoid, and report money laundering and terror financing activities.
Registration Requirements
The US Department of Treasury requires that all MSBs register their business with them. The MSB needs to submit Form 107 with FinCEN within 180 days of establishing its business. MSBs are also required to renew their registration every two years.
Customer Due Diligence
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) is an end-to-end risk assessment process. All banks, financial institutions, and MSBs need to conduct CDD to know their customers’ risk profiles. Customers that turn out to be high risk for the business are then subject to Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), which is a stricter vigilance mechanism.
Know Your Customer
MSBs need to perform proper KYC procedures to verify the identity of their customers. This includes various document verifications such as Driver’s Licence Verification, Social Security Number Verification, and more. KYC procedures also extend to Know Your Business (KYB) where the identity of the ultimate beneficiary of a business is also verified.
Suspicious Activity Report
An extension of the risk-first approach prescribed by the regulatory authorities, Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) require MSBs to file detailed information on transactions conducted by their customers. These reports need to be filed when a customer engages in an activity that is unlike their usual patterns, exceeds certain monetary limits, or violates other triggers set by financial regulators.
How Signzy Helps Money Service Businesses
MSBs primarily function online and need to maintain a streamlined experience to retain customers. All the activities mentioned above can be done manually, but taking such a route can be resource-intensive and prone to errors. This is why it is advisable to integrate a third-party provider’s services into your business KYC and AML verification processes. Signzy’s Marketplace has a plethora of APIs that make regulatory compliance for MSBs a breeze. To see how our various APIs can work into your business processes, book a call with us today.
Conclusion
MSBs operate on similar grounds to banks and other financial institutions, which is why they need to meet similar compliance requirements to these two organizations. While most banks and financial institutions offer a wider range of services, MSBs focus on a few niche segments to provide more tailored experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of a money services business?
Money transfer services, currency exchanges, and remittance services are some of the most popular forms of Money Service Businesses (MSBs).
What is the purpose of MSB?
The purpose of MSBs is to provide more concentrated and tailor-made services to their clientele in the same segments as banks and other financial institutions. Banks and financial institutions provide a wide range of services, while MSBs focus only on a few of these.
How do money service businesses work?
Money Service Businesses convert or transfer funds for their customers. They also provide services specific to businesses like bill and invoice management, and more.