A Significant rise in financial crimes is posing a threat not just for people, but also for financial organisations and regulators.
With an alarming rise in crime rate, especially for crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing, laws and regulations have been rolled out by regulators to keep things in check.
How?
By keeping financial transactions secure using two important processes: Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC).
Although these two processes might seem a little similar, there are some key differences.
Let’s look at what AML and KYC are and how they’re different.
What is AML?
AML is a set of rules that all financial institutions follow to prevent criminals from hiding illegal money. These rules are meant to fight terrorism financing, drug trafficking, and tax evasion.
Banks and insurance companies are required to follow these rules and make sure their systems are not used for illicit activities by identifying customers who might be at risk of money laundering, watching out for suspicious transactions, and reporting unusual activities to the authorities.
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) sets global standards and guidelines to help businesses follow AML rules and create their own AML programs based on their risks to identify any possible suspicious activity/transaction.
For chalking out their AML programs, companies usually follow the below-mentioned steps:
First, appoint a compliance officer and keep an eye on risks.
How?
By continuous due diligence of the clients.
Then, conduct frequent training for employees on AML.
And lastly, create internal rules and monitor their AML programs regularly.
What is KYC?
KYC is another helpful process for financial institutions to protect against these financial crimes.
The main goal here is to gather enough information about customers to understand their risk level and prevent fraud.
What’s the best way banks can decrease the risk of money laundering, terrorist financing, and identity theft?
By knowing their customers well.
How can this be done?
Mandatory KYC checks.
Help businesses make sure their customers are who they say they are.
Help businesses build trust, reduce financial crime, and follow the law by verifying their customers’ identities.
The KYC process, a part of the due diligence, includes collecting information like names, addresses, and ID numbers from documents such as driver’s licenses, or passports to confirm a customer’s identity.
KYC checks can be done in any given situation, like when a customer makes a big transaction, starts a new business relationship, or is suspected of doing something illegal.
The KYC process usually involves checking the user’s identity against outside databases and figuring out how risky they might be.
As we use more and more digital services, industries might need to follow stringent KYC and AML rules to stay safe.
Even if it’s not required for everyone, it’s probably a good idea for any business.
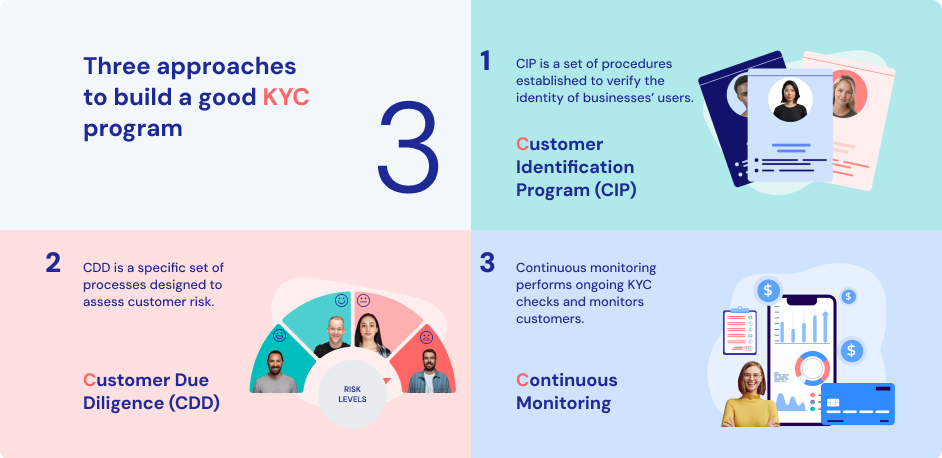
The first approach is the Customer Identification Program (CIP).
This is about ensuring customers are who they say they are.
More the risk, the more checks are needed.
At a minimum, companies collect names, addresses, dates of birth, and ID numbers and sometimes they might also ask for a selfie or check things like IP addresses.
Second approach is implementing the Customer Due Diligence (CDD) process.
This process helps companies understand the risk of money laundering by checking customer identities.
CDD includes:
-Identifying who owns a company
-Imposing regular checks on customers and their transactions
-Implementing checks based on risk-profile of the customer
Due diligence can be simplified for less risky customers while enhanced due diligence is needed for high-risk profiles. For a moderate level of risk, basic due diligence would suffice.
The third approach is Continuous Monitoring.
Companies should keep an eye on customer activity all the time specifically for big cash deposits or unusual transactions.
Ignoring these rules can get companies in trouble with the law.
The specifics of monitoring can change depending on the country in which the company is and the risks involved.
KYC and AML both are important processes that are used by various businesses and banks to address and tackle financial fraud and scams.Although they’re connected with each other, they do serve different functions.
Key Differences between AML and KYC
On the basis of goals,
KYC makes sure that customers are accurately identified before any business transactions are conducted with them whereas AML is about preventing money laundering and terrorism financing.
In terms of focus,
KYC’s emphasizes on collecting and verification of customer identities whereas AML is going one step ahead and focusing on detecting and ceasing any activity that causes suspicion or is related to fraud.
Per compliance requirements,
Although there are always rules and regulations that have to be complied, KYC is simpler because it’s primary function is identifying and verifying customers, however AML is more complex as it has a broader framework and includes many functions like management of risk, reporting any suspicious activity and supervising transactions.
Overall, KYC is one component of ensuring AML compliance.
Understanding the difference between the two is helpful to businesses and banks as it protects them from financial frauds and enables rules to be followed.
Step-wise AML-KYC compliance Process
1. ID verification: To confirm that customers are legitimate.
How can IDs be verified?
Using biometrics like fingerprints or face recognition scans. Addresses are also confirmed to make sure customers are not faking their identity.
2. Due diligence: To understand how risky they might be before letting them sign up.
3. Enhanced due diligence (EDD): An extra step to keep an eye on risky customers and strange transactions to spot possible money laundering.
How to conduct?
By checking their credit history and looking for any negative news about them.
4. Ongoing monitoring: To check in and look for anything out of the ordinary.
It is a continuous process as the level of risk changes with time.
5. Suspicious activity reports (SAR): Acts as a red flag to catch the attention of law enforcement when they spot fishy transactions possibly tied to money laundering or funding terrorism.
6. AML training: Provided to all staff members to recognize and address financial crimes, not solely limited to the compliance team.
Both KYC and AML are required by law, but in different situations.
KYC is about checking who customers are before doing business with them. Here are some examples of when KYC is needed:
– Opening a bank account
– Making an account on shopping websites
– Signing up for cryptocurrency services
– Proving your age for gaming
– Checking in at hotels or airports
– Registering as a patient at a hospital
AML checks, on the other hand, look for signs of financial crimes. Here are some examples of areas when AML is needed:
– Signing up for an overseas bank account
– Using money transfer services
– Making an account at a casino
– Buying real estate
– Law enforcement investigates and punishes people involved in money laundering.
Both KYC and AML are important for many businesses, especially in finance.
How Signzy can help you with AML and KYC verification
A strong KYC-AML compliance program is essential for financial organisations and companies to effectively prevent fraud.
With Signzy, you can ensure your KYC compliance with our KYC API to reduce costs, combat fraud, and increase efficiency.
Similarly, using Signzy’s AML solutions can help improve your AML compliance efforts effortlessly!